1.0 - Fundamental Cloud Concepts¶
Course Overview¶
- AWS Certs add value for technical and non-technical resources.
- Covers:
- Cloud Computing Concepts
- Organization of AWS Global Infrastructure
- Economics of Cloud Computing
- Tools and Services
Understanding Cloud Computing¶
Setting up an AWS Account¶
- aws.amazon.com → Create AWS Account
- Add root email address and account name
- Verify the email address
- Create root user password
- Add contact information and account information e.g. address and name
- Add payment details
- Confirm identity via SMS or call.
- Select support option (free will suffice)
- Go to AWS Management Console → Root User → Login
Set Up Billing Alerts¶
- Account dropdown → Billing management
- Budgets → Create budget → Create from template (if desired)
- Fill out fields as appropriate.
Traditional Data Centres¶
- Consider a company not on the cloud:
- They focus their application release in the US first, in US-based datacentres
- They want to launch in Asia and Europe and require funding to have infrastructure built there to support the needs
- Resources needed include:
- Web servers
- File servers
- Database servers
- Manually setting all this up for each region is long, arduous, and error-strewn.
- Further problems arise when demand scales in any of the pre-existing regions.
- Moving to cloud resolves all of these problems:
- No large upfront investment and planning required
- Use resources as required rather than full unpredictable forecasting
- New data centres and servers can be spun up / torn down as required
- Lower maintenance costs
- Security and compliance burden is alleviated from the organization.
Benefits of Cloud Computing¶
- Trade capital expense for variable expense
- No need for initial investment to build out a datacentre
- Only pay for the resources used and how long they're used for
- Economies of scale
- AWS buys the datacentre resources on a large scale, allowing them to provision the resources on such a price - savings are passed to the customers
- No need to guess capacity - cloud computing can allow scaling on demand.
- Speed and agility increased - resources for testing and deployment can be spun up / torn down at will for minimal costs.
- Reduces time required to maintain infrastructure
- Reduced risk for the organisation around security and compliance
- Provides access to emerging technologies
- No more cost for maintaining data centres - more focus on the employees and other resources
-
Data can be easily switched to different regions.
-
Elasticity: The ability to acquire resources as needed and release when no longer required.
- Reliability: A solution's ability to provide functionality for its users when needed.
Types of Cloud Computing¶
Cloud Computing: The on-demand delivery of compute power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources through a cloud services platform via the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Cloud Computing Models¶
- Models vary based on the control users want to have over the resources
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Any servers users deploy to the cloud
- Can be configured to our desire and users are responsible for maintenance
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- A service preconfigured and available for users
- It can then be customised by users as appropriate e.g. Wordpress, AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Any software users have access to and can use
- Users do not need to consider or maintain the infrastructure.
Cloud Deployment Models¶
- Public Cloud: Deployment to a provider like AWS
- On-Premises Private Cloud: Deployment to a cloud-like platform in a private datacenter (VMware is a common example)
- Hybrid: A combination of both e.g. cloud applications connected to a private data center.
Cloud Computing Scenarios¶
Scenario 1¶
- Several production workloads in its datacentre
- VMware to manage infrastructure in their data centre
- Want to use AWS and integrate it with their data center for new workloads.
- What would they be following?
- Hybrid - Both public and private cloud used.
Scenario 2¶
- Company determining whether to fund a new line of business
- Team looking to monetize a new emerging technology
- New business line requires new infrastructure
- What benefit is most relevant?
- Increased agility and elasticity
- Pay-as-you-go
Scenario 3¶
- Insurance company
- Moving to cloud instead of colocating servers
- Want to have maximum control for security and compliance reasons
- What cloud computing model
- IaaS - Servers can be configured as required and maintained.
AWS Global Infrastructure¶
AWS Regions and Availability Zones¶
- AWS Regions
- Resource / Service deployment location as geographic regions
- Each geographic location has a cluster of data centres
- Availability Zones
- A zone of one or more data centres
- Multiple availability zones are included per AWS region
- All located within the geographic area of the AWS region (sub-regions effectively)
- Have redundant power, networking and connectivity for disaster recovery / high availability purposes.
- Example - US has 6 regions, each with at least 3 availability zones
- Availability: The extent to which an application is fulfilling its intended purpose. Applications that are highly-available are built in a manner where a single failure won't lessen its ability to be fully operational.
Region and Availability Zone Naming¶
- Example: us-east-2a
- Format:
<AREA>-<SUB-AREA>-<NUMBER><Availability Zone Letter>
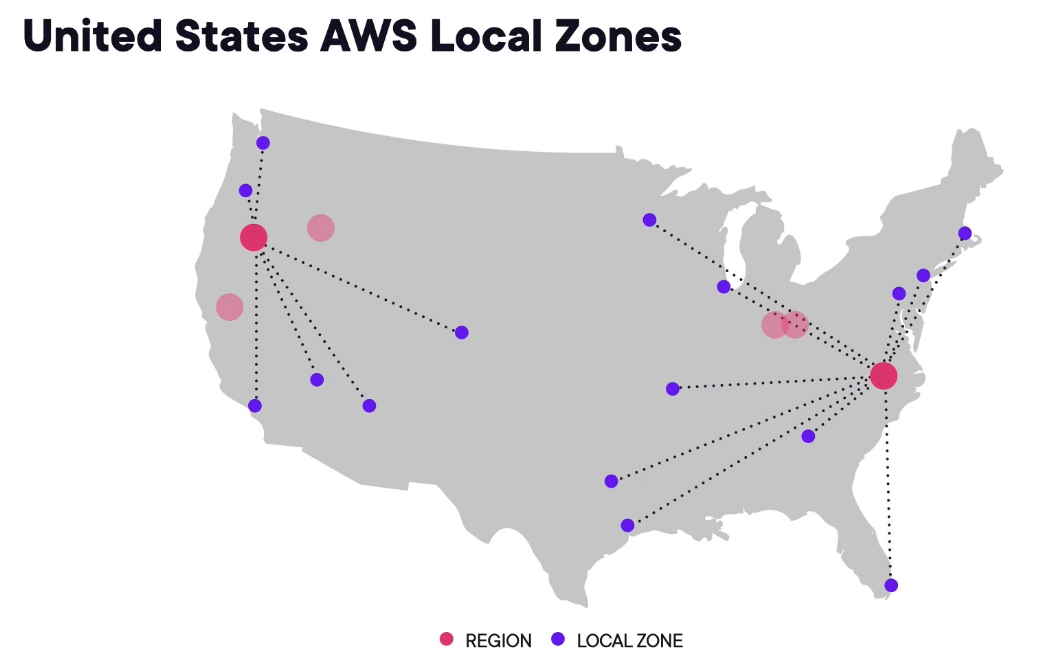
Local and Wavelength Zones¶
Local Zone¶
- Aim to place compute, storage, database, and other AWS services closer to end-users
- An extension of a particular AWS region
- Provides high-bandwidth, secure connections betwen local workloads and those running in AWS region.
- Allows seasmless connection to the full range of in-region services through the same APIs and toolsets.
Wavelength Zones¶
- AWS infrastructure deployments that embed AWS compute and storage services within communication service providers 5G networks.
- Allows application traffic from 5G devices to reach application servers without leaving the telecommunication networks.
AWS Edge Locations¶
Points of Prescence:¶
- Elements of AWS global infrastructure that exist outside of AWS regions.
- Located in or around populated areas - specific AWS services use them to deliver content to end users as quickly as possible.
- 2 Types of infrastructure per point of prescence:
- Edge locations
- Regional edge caches
Edge Locations¶
- Used as nodes of a global content delivery network
- Primarily used by Amazon CloudFront and AWS Route 53
- Allows AWS to serve content from locations closest to users.
Visualizing AWS Global Infrastructure¶
- Global infrastructure
- Edge locations listed per region amongst other information
Global Infrastructure Scenarios¶
Global Infrastructure Scenario 1¶
- Looking to transfer to AWS with a few workloads
- Requirement to store backup data in multiple geographic areas
- What element of AWS Global Infrastructure will help best?
- AWS Regions - Regions are geographical areas e.g. could store data in one and run the applications in another.
Global Infrastructure Scenario 2¶
- Content served across the world
- Wanting to optimize performance to users worldwide
- Want to leverage a content delivery network
- What element is best suited to help this from AWS infrastructure?
- Edge Locations
Global Infrastructure Scenario 3¶
- Legacy applications transitioning to AWS
- 99.5% uptime required
- Don't want issues at single datacentres to cause outages
- What element of the global infrastructure will help?
- Availability zones
Understanding Cloud Economics¶
Economics of the Cloud¶
- Capitalized Expenditure (CapEx):
- Upfront costs or investments to attain a fixed asset
- Example for building a datacenter would be the building, servers, etc.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx)
- Day-to-day business activities
- Example being maintenance costs
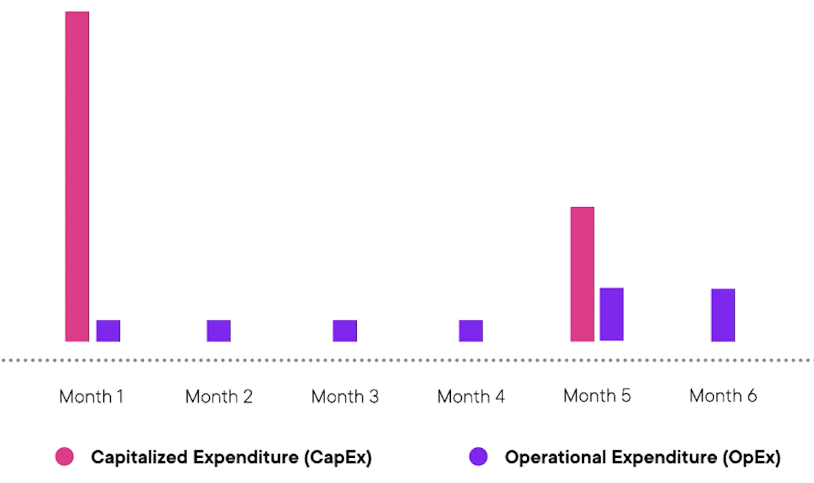
Handling Demand in Data Centre¶
- As application usage grows, data centres need to grow with it in capacity
- When first launched, there would be a lot of unused capacity
- Eventually, demand would exceed capacity → data centre capacity needs to be increased
- In terms of CapEx vs OpEx
- CapEx starts out large due to initial acquiring
- OpEx maintained at generally consistent levels.
- Any time the capacity needs to be increased, CapEx goes up.
Handling Demand in the Cloud¶
- Companies in the cloud can ensure the capacity is always "just enough" to ensure the demand is met
- As the cloud resources are being leveraged, there is no CapEx costs, instead, the OpEx costs vary depending on the application usage adn the demand.
Financial Implications¶
| Own Data Centre | Cloud Infrastructure |
|---|---|
| Large CapEx | No upfront investment |
| Potential for under used capacity or unmet demand | Pay as you go for infrastructure (OpEx) |
| Increasing capacity takes time and additional investment (CapEx) | Capacity scales to meet user demand and can be immediately provisioned |
| Monthly costs will map to predicted infrastructure needs | Costs mirror usage levels - use more, pay more, use less, pay less etc. |
Organizing and Optimizing AWS Costs¶
- AWS Cost Explorer
- User Interface for AWS Cost Analysis
- Provides breakdowns per:
- Service
- Cost tag
- Provides 3-monthly forecasting.
- Provides recommendations for cost optimizations.
- Data accessible via API
- AWS Budgets
- Takes data from AWS Cost explorer to plan and track usage across services.
- Tracks cost per service, service usage, reserved instance utilisation and coverage, and savings plans utilisation and coverage.
- AWS Cost Planning Tools:
- AWS Pricing Calculator
- Allows in-depth analysis of cost for multiple AWS services for cloud-based workloads.
- AWS Migration Hub:
- Provides recommendations and a business case for transitioning workloads to the cloud.
- Deprecated Tools:
- AWS TCO Calculator - Enabled estimated savings for using cloud infrastructure to be determined
- AWS Simple Monthly Calculator
- AWS Resource Tags:
- Metadata assigned to specific AWS resources
- Key/Value
- Common usage includes department, environment, or project.
- Cost allocation can report can include costs grouped by active tags.
- AWS Organizations:
- Allows organisations to manage multiple accounts under a single master account
- Offers consolidated billing for all accounts.
- Facilitates centralized logging and security standard implementation.
Building a Business Case for the Cloud¶
- Steps to build a business case:
- Analyze the current workloads
- Forecast the infrastructure needs
- Create a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for both options.
- Tools available:
- AWS Migration Hub - Gathers information from multiple services and tools in AWS to forecast required infrastructure.
- Migration Evaluator - Similar to the migration hub but provides a more in-depth analysis.
AWS Pricing Calculator¶
- Used to estimate future workloads
- Accessible at calculator.aws
- Create Estimate → Fill out desired fields i.e.:
- Location or Service Type
- Configure Services:
- Quick Estimate or Advanced Estimate
- Service Details e.g. for EC2 check the resources
- Expected utilisation
- Pricing Strategies
- Any sub-services e.g. Elastic Block Storage (EBS) for EC2 Instances
- Upfront, Monthly and Total 12 month costs are provided upon completion.
- Any additional services can then be added to the estimate as required e.g. Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL
- The estimate can then be exported or shared.
- Additionally estimates can be grouped within the estimate e.g. group based on "application" or "function".
Reviewing Costs - Costs Explorer¶
- AWS Accounts → Profile Dropdown → Billing Dashboard → Cost Explorer → Launch Cost Explorer
- Provides initial overviews such as:
- Current monthly cost
- Forecast month-end costs
- Daily cost grouping
- Can be filtered per AWS Service, region, resource, etc.
- From LHS pane → Reports
- Includes reports such as:
- Monthly costs per account
- Daily costs
Applying Cloud Economics¶
Cloud Economics Scenario 1¶
- Multiple departments within AWS
- FInance requesting clean separation of AWS costs within departments
- All resources are within a single AWS Account
- What approach would meet this need for future costs with minimal effort?
- Resource tags
Cloud Economics Scenario 2¶
- Company considering transition to the cloud
- 2 physical data centres
- Stakeholders wanting financial insight
- Which approach to make a business case?
- Use the migration hub or migration evaluator
Cloud Economics Scenario 3¶
- Web developer
- Looking to move site to cloud.
- Financial estimates needed.
- What approach?
- Use the pricing calculator.
Supporting AWS Infrastructure¶
Support Resources¶
- AWS support → Allows support tickets to be submitted
- Includes Personal Health Dashboard. and Trusted Advisor
- AWS Support:
- Enables support from AWS resources for workloads running in the cloud
- Provided in different tiers based on need and scope
- Includes tools to provide automated answers and recommendations
- AWS Personal Health Dashboard
- Provides alerts and remediation guidance when events occur in AWS that may impact you e.g. regional outages
- AWS Trusted Advisor
- An automated tool to check AWS usage against best practices
- Accessible from the AWS console
- Provides multiple checks based on the support plan tier, in addition to core checks
- Checks include:
- Cost optimization
- Performance
- Security
- Fault Tolerance
- Service Limits
AWS Support Plan Tiers¶
- Support plan tiers are based on:
- Communication method
- Response Time
- Cost
- Type of guidance offered
- Basic Support
- Provided for all customers
- Access to trusted advisor (7 core checks)
- Documentation, forums, and 24x7 customer service access
- AWS Personal health dashboard
- Free
- Developer Support
- Everything in basic
- Includes access to support engineers via email during business hours
- 1 Primary contact
- $29/month
- Business support
- All of developer support
- Full set of trusted advisor checks
- 24x7 phone, email and chat access to support engineers
- unlimited contacts for support requests
- Third-party software support provided
- $100/month (based on AWS usage)
- Enterprise Support:
- All features of business support
- Includes technical account manager (TAM)
- Includes concierge support team
- $15,000/month
- Support Response Times dependent upon the nature of the request:
- General Guidance
- System Impaired
- Production System Impaired
- Production System Down
- Business-Critical System Down
AWS Support Tools¶
- AWS Console → Health View and Trusted Advisor are automatically included as widgets
- Also accessible from search bar
- Trusted Advisor:
- Shows summary and recommendation categories
- Recommendations only provided based on checks available.
- Details on recommended actions provided, with remediation steps.
- Will show checks which aren't included for reference.
- Checks can be downloaded.
- AWS Health Dashboard
- Service health dashboard
- Issue and events logs
- Service history.
When You Need Help¶
- Resources available for help:
- AWS Quickstart - Provides steps for standard platform deployments
- AWS Partner Network Consulting Partners - 3rd Party Consultants that are Partners with AWS
- AWS Professional Services
Infrastructure Support Scenarios¶
Infrastructure Support Scenario 1¶
- Moving multiple workloads into AWS
- One workload is mission-critical
- 24/7 support needed
- What support level? - Business Support
Infrastructure Support Scenario 2¶
- Evaluating AWS for future or workloads
- Workloads supports multiple offices globally
- Email text or call to support needed.
- Response within 15 mins needed.
- What support plan? Enterprise
Infrastructure Support Scenario 3¶
- Account for a personal project
- No Technical Guidance needed
- Want access to Trusted Advisor etc
- Basic Support plan needed.