5.2 - Using Crash Diagnostics
Objectives
- Describe the purpose of Crash Diagnostics
Crash Diagnostics (Crashd)
- A command-line tool that facilitates investigation and troubleshooting of unhealthy or unresponsive Kubernetes clusters
- Only available on Linux or Mac OS
- Runs a series of scripts that collect Kubernetes API output, node logs, node CLI outputs through SSH to assess the health of the clusters
Diagnostic Scripts
- Scripts included in crashd written in Starlark (a dialect of Python)
- Crashd exposes commonly used operations as Starlark functions used to build diagnostic scripts
- Examples:
- Run kubectl and collect specified resources:
kube_capture (what="objects", kinds=["deployments", "services"], namespaces=["default"])
- Run a command through SSH on a particular node:
capture(cmd="df -h /", resources=nodes)
Default Diagnostics Script
- Crashd provides a default diagnostics script covering common use cases that:
- Accepting arguments to specify what to collect
- Collects bootstrap management and workload cluster information
- Outputs an archive file containing all requested information
Passing Arguments to the Diagnostics Scripts
- Two typical methods used:
- An args file, used via
--args-file <args file>
- Specifying the args in key-value pairs in the CLI e.g.
--args key1=value1,key2=value2
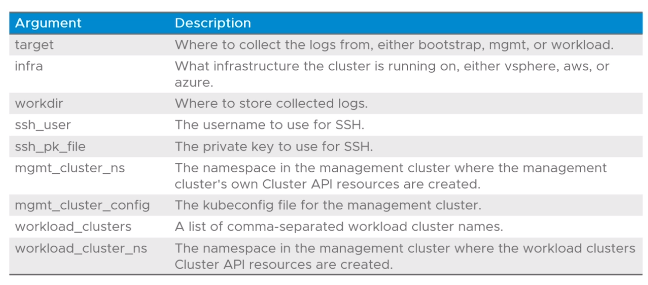
Default Diagnostic Script Arguments
- The default diagnostics script accepts the following arguments amongst many others
Running Crash Diagnostics
- Depending on whether using an args file or not, crashd is initiated via the following:
- Passing the args from a file:
crashd run --args-file <args file> <crashd script.crsh>
- Same as above but override the target and workload_cluster parameters:
crashd run --args-file <args file> --args target=workload,workload_cluster=tkc-01 diagnostics.crsh
