6.0 - Ansible Modules¶
06.1 - Ansible Modules¶
Notes¶
- Modules are categorised based on functionalities e.g
- System - Commands based on the host system e.g. start/stop service
- Commands - Used to execute commands or scripts on hosts
- Files - Used to execute file-specific commands e.g. find, copy, replace
- Database - Used to interact with databases such as MongoDB, MSSQL, MySQL
- Cloud - Used to interact with cloud providers like AWS, Azure, GCP, Linode, Digital Ocean.
- Windows - Commands to help use Ansible in a windows environment, be it working with files, user management, executing commands.
- This is a non-exhaustive list - many more modules can be viewed in the Ansible documentation, with details on how to use each provided.
Command¶
- Used to execute a command on a remote node
- Parameters include:
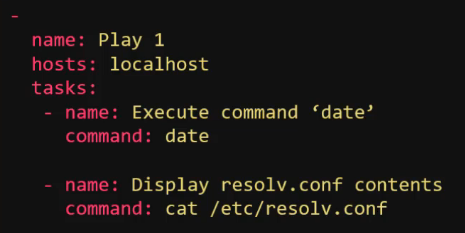
- Example Playbook:
Example playbook to execute the date command and run the cat command on a desired file.
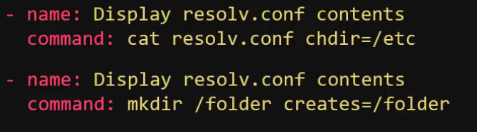
- Creates parameter is used to perform a check if the folder or file exists before running the command
- chdir requests that ansible changes directory before the command is ran
- free_form - the command module takes a free form command to run; no parameters are required
- Not all commands support free-form parameters, example, copy requires a source and target dir to be specified.
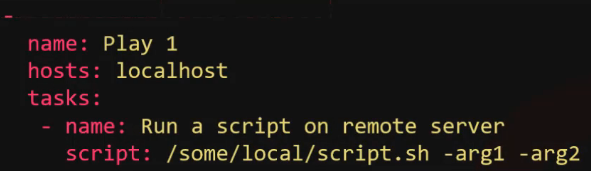
Script¶
- Used to run a local script on a remote node after transferring it.
- Example playbook:
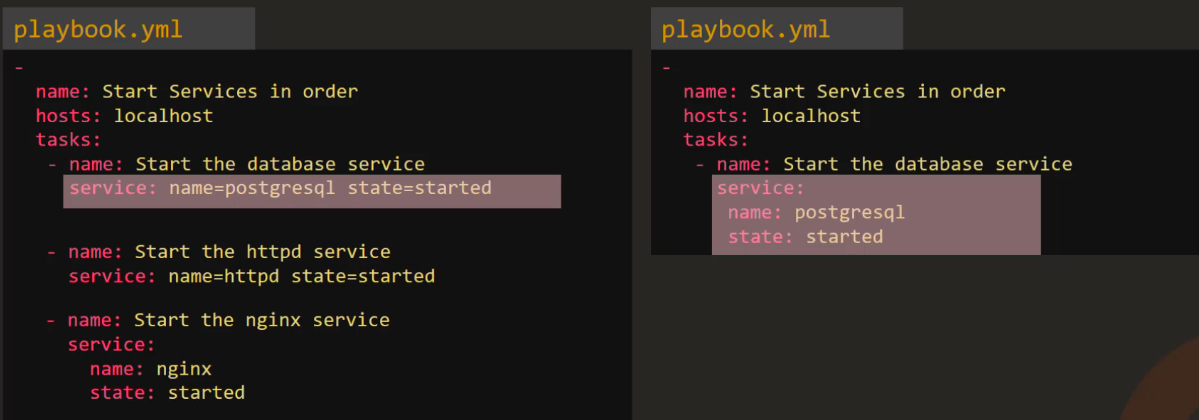
Service¶
- Used to manage services on the system e.g. stop, start, restart
- Example playbooks for this can be done in one of two manners:
- Question: Why write the state as "started" and not "start"?
- Not instructing ansible to start the service, we are asking ansible to ensure that it is started i.e. if it's not started - start it
- This leads to the idempotency of ansible modules:
- Idempotency - An operation is idempotent if the result of performing it once is exactly the same as the result of performing it repeatedly without any intervening actions
- In general, Ansible's idea is to be able to run a playbook, when running it again, everything should return "as expected", if not, Ansible will make it so.
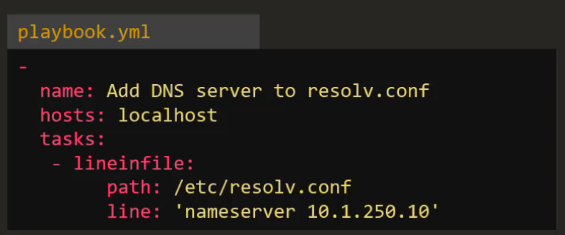
Lineinfile¶
- Searches for a line in a file and replaces it or adds it if it doesn't exist
- Example playbook:
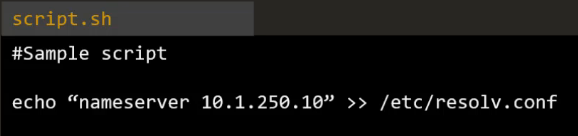
- Note that this action IN THEORY could be achieved by running a script like this:
- However, this would repeatedly add the same entry to /etc/resolv.conf rather than replace it or not add it if found. By contrast the idempotency of Ansible means that if this task is ran as part of a playbook, the entry is added once and only once if it's not found.
6.2 - Introduction to Plugins¶
Overview¶
- Ansible plugins aim to provide additional functionality and customisation options beyond the core features.
- Plugins extend or modify the core functionality of ansible, such as inventory, modules, and callbacks.
- Plugins can be found as any of:
- Inventory Plugins (e.g. Dynamic Inventory)
- Module Plugins (e.g. provision custom cloud configuration)
- Action Plugins (e.g. define a series of high-level tasks to help enhance consistency in the configuration)
- Callback Plugins - provide hooks into ansible's execution lifecycle, facilitating custom actions during playbook execution.
- Lookup Plugins (typically used with Databases)
- Filter Plugins
- Connection Plugins
- Each plugin comes with their own parameters and configuration.
6.3 - Modules and Plugins Index¶
Overview¶
- The module and plugin index aims to act as a hub for searching plugins and modules to be added to playbooks.
- Each comes with documentation for usage, examples, and additional supporting documentation.
- Index link
- The index offers:
- Search and filtering
- Detailed documentation per plugin
- Version compatability guidance and considerations
- Community contributions for support and contribution guidance.
06.2 - Ansible Modules Coding Exercises¶
Notes¶
Q1¶
Update the playbook with a play to Execute a script on all web server nodes. The script is located at /tmp/install_script.sh
Use the Script module
- name: 'Execute a script on all web server nodes'
hosts: web_nodes
tasks:
- name: 'Execute a script on all web server nodes'
script: /tmp/install_script.sh
Q2¶
Update the playbook to add a new task to start httpd services on all web nodes
Use the Service module
-
name: 'Execute a script on all web server nodes'
hosts: web_nodes
tasks:
-
name: 'Execute a script on all web server nodes'
script: /tmp/install_script.sh
- name: 'start http services on all web server nodes'
service:
name: httpd
state: started
Q3¶
Update the playbook to add a new task in the beginning to add an entry into /etc/resolv.conf file for hosts. The line to be added is nameserver 10.1.250.10
Note: The new task must be executed first, so place it accordingly.
Use the Lineinfile module
-
name: 'Execute a script on all web server nodes'
hosts: web_nodes
tasks:
- name: 'Add enntry to /etc/resolv.conf file'
lineinfile:
path: /etc/resolv.conf
line: 'nameserver 10.1.250.10'
-
name: 'Execute a script'
script: /tmp/install_script.sh
-
name: 'Start httpd service'
service:
name: httpd
state: present
Q4¶
Update the playbook to add a new task at second position (right after adding entry to resolv.conf) to create a new web user.
Use the user module for this. User details to be used are given below:Username: web_useruid: 1040group: developers
-
name: 'Execute a script on all web server nodes and start httpd service'
hosts: web_nodes
tasks:
-
name: 'Update entry into /etc/resolv.conf'
lineinfile:
path: /etc/resolv.conf
line: 'nameserver 10.1.250.10'
- name: 'add user web_user'
user:
name: web_user
uid: 1040
group: developers
- name: 'Execute a script'
script: /tmp/install_script.sh
-
name: 'Start httpd service'
service:
name: httpd
state: present