3.4 - Managing Tanzu Kubernetes Clusters
Learning Objectives
Describe the commands available for working with Tanzu Kubernetes clusters.
Granting Authenticated Access to a Cluster
Running tanzu cluster kubeconfig get <cluster name> generates the kubeconfig file that can be shared with users requiring access to the cluster.
The kubeconfig file is configured with instructions that run the Tanzu CLI and trigger the Pinniped authentication workflow.
Though the process authenticates a user to the cluster, the user will still require permissions to be granted for them on the cluster to be able to interact with the Kubernetes API resources.
Granting Access to Cluster Resources
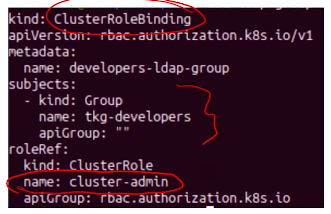
To allow authorization of an authenticated user, RoleBindings or CLusterRoleBindings need to be utilised.
These are standard Kubernetes resources that allow permissions from a "role" or "clusterrole" to be bound to a user account.
Example:
Scaling Clusters
To scale clusters, use the scale command and include the required controlplane-machine-count and worker-machine-count values
Example:
tanzu cluster scale <cluster name> --controlplane-machine-count <value> --worker-machine-count <value>
From this, the Tanzu CLI modifies the Cluster API spec of the cluster; triggering the Cluster API controllers to create the new nodes
Scaling can be done up or down
Control plane nodes can ONLY be scaled to an ODD number of nodes - aims to prevent quorum issues during etcd leader elections.
Scaling Management Clusters
As management clusters run in the tkg-system namespace, the --namespace flag must be specified when scaling a management cluster.
Example:
tanzu cluster scale <mgmt cluster name> --controlplane-machine-count <value> --worker-machine-count <value> --namespace <namespace>
Scaling management clusters isn't typically needed - management workloads don't consume much resources.
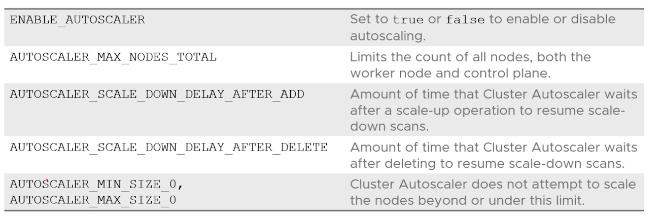
Cluster Autoscaler
Note: The native Kubernetes Autoscaler must be enabled for any of these parameters to take effect.
Machine Health Checks
MachineHealthCheck - a controller that provides node health monitoring and auto-repair for Tanzu Kubernetes clusters.
Monitors for the following conditions:
Ready State
MemoryPressure
DiskPressure
PIDPressure
NetworkUnavailable
If a node status reports the condition for a particular amount of time, the node is considered unhealthy and is recreated by Cluster API.
Configuring Machine Health Checks
Each created cluster must have ENABLE_MGC set to true or false to enable or disable MachineHealthCheck
This can be modified by the Tanzu CLI
tanzu cluster machinehealthcheck set <parameters and args>Example: tanzu cluster machinehealthcheck set <cluser name> --unhealthy-conditions "Ready:False:5m,Ready:Unknown:5m"
If False or Unknown is reported as the ready status for 5 mins, the node will be recreated.